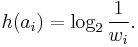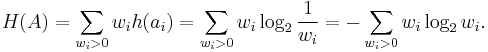Huffman coding

| Char | Freq | Code |
|---|---|---|
| space | 7 | 111 |
| a | 4 | 010 |
| e | 4 | 000 |
| f | 3 | 1101 |
| h | 2 | 1010 |
| i | 2 | 1000 |
| m | 2 | 0111 |
| n | 2 | 0010 |
| s | 2 | 1011 |
| t | 2 | 0110 |
| l | 1 | 11001 |
| o | 1 | 00110 |
| p | 1 | 10011 |
| r | 1 | 11000 |
| u | 1 | 00111 |
| x | 1 | 10010 |
In computer science and information theory, Huffman coding is an entropy encoding algorithm used for lossless data compression. The term refers to the use of a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file) where the variable-length code table has been derived in a particular way based on the estimated probability of occurrence for each possible value of the source symbol. It was developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Ph.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes."
Huffman coding uses a specific method for choosing the representation for each symbol, resulting in a prefix code (sometimes called "prefix-free codes", that is, the bit string representing some particular symbol is never a prefix of the bit string representing any other symbol) that expresses the most common source symbols using shorter strings of bits than are used for less common source symbols. Huffman was able to design the most efficient compression method of this type: no other mapping of individual source symbols to unique strings of bits will produce a smaller average output size when the actual symbol frequencies agree with those used to create the code. A method was later found to design a Huffman code in linear time if input probabilities (also known as weights) are sorted.
For a set of symbols with a uniform probability distribution and a number of members which is a power of two, Huffman coding is equivalent to simple binary block encoding, e.g., ASCII coding. Huffman coding is such a widespread method for creating prefix codes that the term "Huffman code" is widely used as a synonym for "prefix code" even when such a code is not produced by Huffman's algorithm.
Although Huffman's original algorithm is optimal for a symbol-by-symbol coding (i.e. a stream of unrelated symbols) with a known input probability distribution, it is not optimal when the symbol-by-symbol restriction is dropped, or when the probability mass functions are unknown, not identically distributed, or not independent (e.g., "cat" is more common than "cta"). Other methods such as arithmetic coding and LZW coding often have better compression capability: both of these methods can combine an arbitrary number of symbols for more efficient coding, and generally adapt to the actual input statistics, the latter of which is useful when input probabilities are not precisely known or vary significantly within the stream. However, the limitations of Huffman coding should not be overstated; it can be used adaptively, accommodating unknown, changing, or context-dependent probabilities. In the case of known independent and identically-distributed random variables, combining symbols together reduces inefficiency in a way that approaches optimality as the number of symbols combined increases.
Contents |
History
In 1951, David A. Huffman and his MIT information theory classmates were given the choice of a term paper or a final exam. The professor, Robert M. Fano, assigned a term paper on the problem of finding the most efficient binary code. Huffman, unable to prove any codes were the most efficient, was about to give up and start studying for the final when he hit upon the idea of using a frequency-sorted binary tree and quickly proved this method the most efficient.
In doing so, the student outdid his professor, who had worked with information theory inventor Claude Shannon to develop a similar code. Huffman avoided the major flaw of the suboptimal Shannon-Fano coding by building the tree from the bottom up instead of from the top down.
Problem definition
Informal description
- Given
- A set of symbols and their weights (usually proportional to probabilities).
- Find
- A prefix-free binary code (a set of codewords) with minimum expected codeword length (equivalently, a tree with minimum weighted path length from the root).
Formalized description
Input.
Alphabet 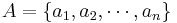 , which is the symbol alphabet of size
, which is the symbol alphabet of size 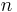 .
.
Set 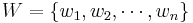 , which is the set of the (positive) symbol weights (usually proportional to probabilities), i.e.
, which is the set of the (positive) symbol weights (usually proportional to probabilities), i.e. 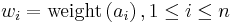 .
.
Output.
Code 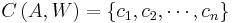 , which is the set of (binary) codewords, where
, which is the set of (binary) codewords, where 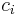 is the codeword for
is the codeword for 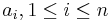 .
.
Goal.
Let 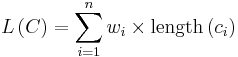 be the weighted path length of code
be the weighted path length of code  . Condition:
. Condition: 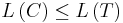 for any code
for any code 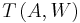 .
.
Samples
| Input (A, W) | Symbol (ai) | a | b | c | d | e | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weights (wi) | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.29 | = 1 | |
| Output C | Codewords (ci) | 010 | 011 | 11 | 00 | 10 | |
| Codeword length (in bits) (li) |
3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Weighted path length (li wi ) |
0.30 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 0.58 | L(C) = 2.25 | |
| Optimality | Probability budget (2-li) |
1/8 | 1/8 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | = 1.00 |
| Information content (in bits) (−log2 wi) ≈ |
3.32 | 2.74 | 1.74 | 2.64 | 1.79 | ||
| Entropy (−wi log2 wi) |
0.332 | 0.411 | 0.521 | 0.423 | 0.518 | H(A) = 2.205 |
For any code that is biunique, meaning that the code is uniquely decodeable, the sum of the probability budgets across all symbols is always less than or equal to one. In this example, the sum is strictly equal to one; as a result, the code is termed a complete code. If this is not the case, you can always derive an equivalent code by adding extra symbols (with associated null probabilities), to make the code complete while keeping it biunique.
As defined by Shannon (1948), the information content h (in bits) of each symbol ai with non-null probability is
The entropy H (in bits) is the weighted sum, across all symbols ai with non-zero probability wi, of the information content of each symbol:
(Note: A symbol with zero probability has zero contribution to the entropy. When w = 0, 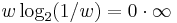 is an indefinite form; so by L'Hôpital's rule:
is an indefinite form; so by L'Hôpital's rule:
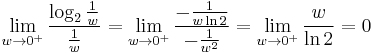 .
.
For simplicity, symbols with zero probability are left out of the formula above.)
As a consequence of Shannon's source coding theorem, the entropy is a measure of the smallest codeword length that is theoretically possible for the given alphabet with associated weights. In this example, the weighted average codeword length is 2.25 bits per symbol, only slightly larger than the calculated entropy of 2.205 bits per symbol. So not only is this code optimal in the sense that no other feasible code performs better, but it is very close to the theoretical limit established by Shannon.
Note that, in general, a Huffman code need not be unique, but it is always one of the codes minimizing 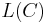 .
.
Basic technique

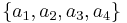 with probability
with probability 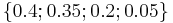 . A binary tree is generated from left to right taking the two less probable symbols, putting them together to form another equivalent symbol having a probability that equals the sum of the two symbols. The process is repeated until there is just one symbol. The tree can then be read backwards, from right to left, assigning different bits to different branches. The final Huffman code is:
. A binary tree is generated from left to right taking the two less probable symbols, putting them together to form another equivalent symbol having a probability that equals the sum of the two symbols. The process is repeated until there is just one symbol. The tree can then be read backwards, from right to left, assigning different bits to different branches. The final Huffman code is:
| Symbol | Code |
|---|---|
| a1 | 0 |
| a2 | 10 |
| a3 | 110 |
| a4 | 111 |
The technique works by creating a binary tree of nodes. These can be stored in a regular array, the size of which depends on the number of symbols, 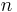 . A node can be either a leaf node or an internal node. Initially, all nodes are leaf nodes, which contain the symbol itself, the weight (frequency of appearance) of the symbol and optionally, a link to a parent node which makes it easy to read the code (in reverse) starting from a leaf node. Internal nodes contain symbol weight, links to two child nodes and the optional link to a parent node. As a common convention, bit '0' represents following the left child and bit '1' represents following the right child. A finished tree has up to
. A node can be either a leaf node or an internal node. Initially, all nodes are leaf nodes, which contain the symbol itself, the weight (frequency of appearance) of the symbol and optionally, a link to a parent node which makes it easy to read the code (in reverse) starting from a leaf node. Internal nodes contain symbol weight, links to two child nodes and the optional link to a parent node. As a common convention, bit '0' represents following the left child and bit '1' represents following the right child. A finished tree has up to 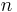 leaf nodes and
leaf nodes and 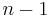 internal nodes. A Huffman tree that omits unused symbols produces the most optimal code lengths.
internal nodes. A Huffman tree that omits unused symbols produces the most optimal code lengths.
The process essentially begins with the leaf nodes containing the probabilities of the symbol they represent, then a new node whose children are the 2 nodes with smallest probability is created, such that the new node's probability is equal to the sum of the children's probability. With the previous 2 nodes merged into one node (thus not considering them anymore), and with the new node being now considered, the procedure is repeated until only one node remains, the Huffman tree.
The simplest construction algorithm uses a priority queue where the node with lowest probability is given highest priority:
- Create a leaf node for each symbol and add it to the priority queue.
- While there is more than one node in the queue:
- Remove the two nodes of highest priority (lowest probability) from the queue
- Create a new internal node with these two nodes as children and with probability equal to the sum of the two nodes' probabilities.
- Add the new node to the queue.
- The remaining node is the root node and the tree is complete.
Since efficient priority queue data structures require O(log n) time per insertion, and a tree with n leaves has 2n−1 nodes, this algorithm operates in O(n log n) time.
If the symbols are sorted by probability, there is a linear-time (O(n)) method to create a Huffman tree using two queues, the first one containing the initial weights (along with pointers to the associated leaves), and combined weights (along with pointers to the trees) being put in the back of the second queue. This assures that the lowest weight is always kept at the front of one of the two queues:
- Start with as many leaves as there are symbols.
- Enqueue all leaf nodes into the first queue (by probability in increasing order so that the least likely item is in the head of the queue).
- While there is more than one node in the queues:
- Dequeue the two nodes with the lowest weight by examining the fronts of both queues.
- Create a new internal node, with the two just-removed nodes as children (either node can be either child) and the sum of their weights as the new weight.
- Enqueue the new node into the rear of the second queue.
- The remaining node is the root node; the tree has now been generated.
It is generally beneficial to minimize the variance of codeword length. For example, a communication buffer receiving Huffman-encoded data may need to be larger to deal with especially long symbols if the tree is especially unbalanced. To minimize variance, simply break ties between queues by choosing the item in the first queue. This modification will retain the mathematical optimality of the Huffman coding while both minimizing variance and minimizing the length of the longest character code.
Here's an example using the French subject string "j'aime aller sur le bord de l'eau les jeudis ou les jours impairs":
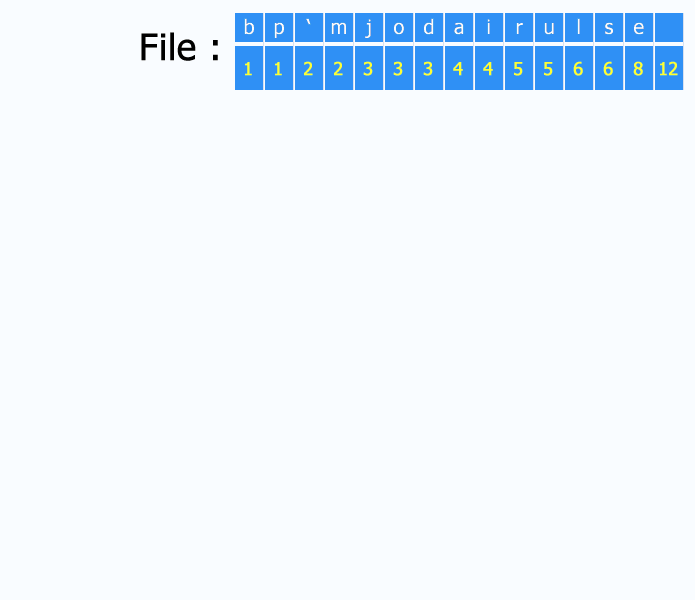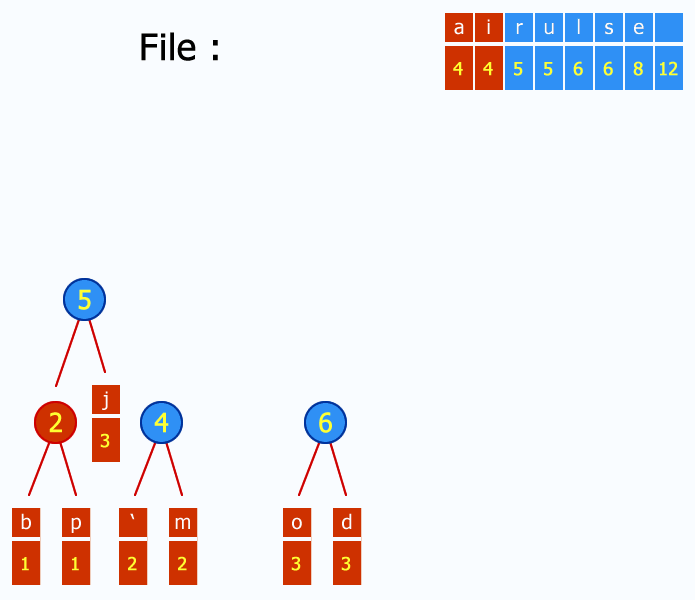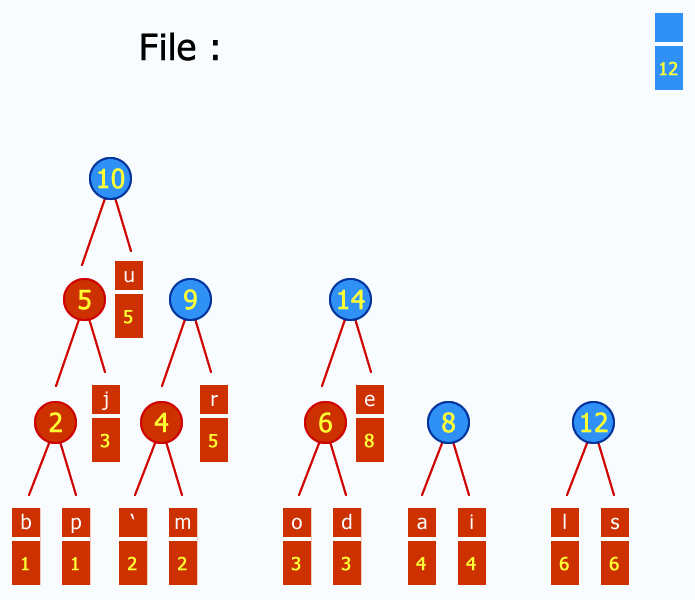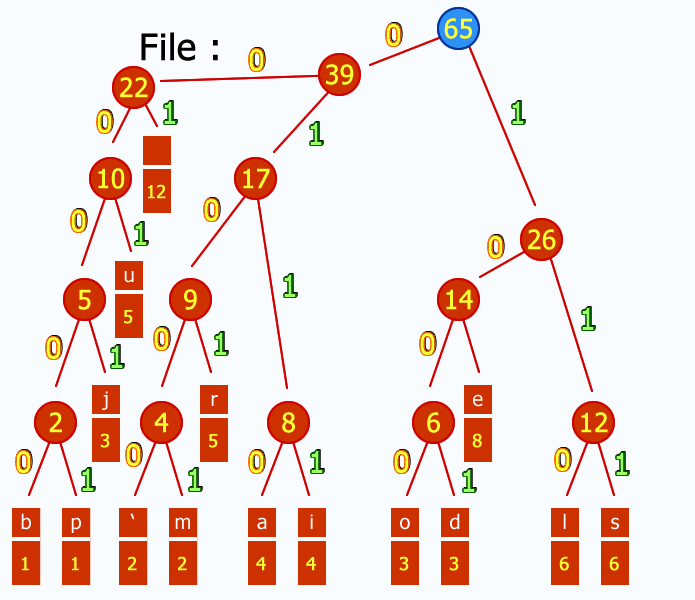
Main properties
The probabilities used can be generic ones for the application domain that are based on average experience, or they can be the actual frequencies found in the text being compressed. (This variation requires that a frequency table or other hint as to the encoding must be stored with the compressed text; implementations employ various tricks to store tables efficiently.)
Huffman coding is optimal when the probability of each input symbol is a negative power of two. Prefix codes tend to have inefficiency on small alphabets, where probabilities often fall between these optimal points. "Blocking", or expanding the alphabet size by grouping multiple symbols into "words" of fixed or variable-length before Huffman coding helps both to reduce that inefficiency and to take advantage of statistical dependencies between input symbols within the group (as in the case of natural language text). The worst case for Huffman coding can happen when the probability of a symbol exceeds 2−1 = 0.5, making the upper limit of inefficiency unbounded. These situations often respond well to a form of blocking called run-length encoding; for the simple case of Bernoulli processes, Golomb coding is a provably optimal run-length code.
Arithmetic coding produces some gains over Huffman coding, although arithmetic coding has higher computational complexity. Also, arithmetic coding was historically a subject of some concern over patent issues. However, as of mid-2010, various well-known effective techniques for arithmetic coding have passed into the public domain as the early patents have expired.
Variations
Many variations of Huffman coding exist, some of which use a Huffman-like algorithm, and others of which find optimal prefix codes (while, for example, putting different restrictions on the output). Note that, in the latter case, the method need not be Huffman-like, and, indeed, need not even be polynomial time. An exhaustive list of papers on Huffman coding and its variations is given by "Code and Parse Trees for Lossless Source Encoding"[1].
n-ary Huffman coding
The n-ary Huffman algorithm uses the {0, 1, ... , n − 1} alphabet to encode message and build an n-ary tree. This approach was considered by Huffman in his original paper. The same algorithm applies as for binary (n equals 2) codes, except that the n least probable symbols are taken together, instead of just the 2 least probable. Note that for n greater than 2, not all sets of source words can properly form an n-ary tree for Huffman coding. In this case, additional 0-probability place holders must be added. This is because the tree must form an n to 1 contractor; for binary coding, this is a 2 to 1 contractor, and any sized set can form such a contractor. If the number of source words is congruent to 1 modulo n-1, then the set of source words will form a proper Huffman tree.
Adaptive Huffman coding
A variation called adaptive Huffman coding involves calculating the probabilities dynamically based on recent actual frequencies in the sequence of source symbols, and changing the coding tree structure to match the updated probability estimates.
Huffman template algorithm
Most often, the weights used in implementations of Huffman coding represent numeric probabilities, but the algorithm given above does not require this; it requires only a way to order weights and to add them. The Huffman template algorithm enables one to use any kind of weights (costs, frequencies, pairs of weights, non-numerical weights) and one of many combining methods (not just addition). Such algorithms can solve other minimization problems, such as minimizing ![\max_i\left[w_{i}+\mathrm{length}\left(c_{i}\right)\right]](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/93f6a8cf382b97ccad472e4b2816479e.png) , a problem first applied to circuit design [2].
, a problem first applied to circuit design [2].
Length-limited Huffman coding
Length-limited Huffman coding is a variant where the goal is still to achieve a minimum weighted path length, but there is an additional restriction that the length of each codeword must be less than a given constant. The package-merge algorithm solves this problem with a simple greedy approach very similar to that used by Huffman's algorithm. Its time complexity is 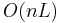 , where
, where 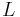 is the maximum length of a codeword. No algorithm is known to solve this problem in linear or linearithmic time, unlike the presorted and unsorted conventional Huffman problems, respectively.
is the maximum length of a codeword. No algorithm is known to solve this problem in linear or linearithmic time, unlike the presorted and unsorted conventional Huffman problems, respectively.
Huffman coding with unequal letter costs
In the standard Huffman coding problem, it is assumed that each symbol in the set that the code words are constructed from has an equal cost to transmit: a code word whose length is N digits will always have a cost of N, no matter how many of those digits are 0s, how many are 1s, etc. When working under this assumption, minimizing the total cost of the message and minimizing the total number of digits are the same thing.
Huffman coding with unequal letter costs is the generalization in which this assumption is no longer assumed true: the letters of the encoding alphabet may have non-uniform lengths, due to characteristics of the transmission medium. An example is the encoding alphabet of Morse code, where a 'dash' takes longer to send than a 'dot', and therefore the cost of a dash in transmission time is higher. The goal is still to minimize the weighted average codeword length, but it is no longer sufficient just to minimize the number of symbols used by the message. No algorithm is known to solve this in the same manner or with the same efficiency as conventional Huffman coding.
Optimal alphabetic binary trees (Hu-Tucker coding)
In the standard Huffman coding problem, it is assumed that any codeword can correspond to any input symbol. In the alphabetic version, the alphabetic order of inputs and outputs must be identical. Thus, for example, 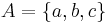 could not be assigned code
could not be assigned code 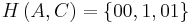 , but instead should be assigned either
, but instead should be assigned either 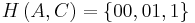 or
or 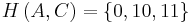 . This is also known as the Hu-Tucker problem, after the authors of the paper presenting the first linearithmic solution to this optimal binary alphabetic problem, which has some similarities to Huffman algorithm, but is not a variation of this algorithm. These optimal alphabetic binary trees are often used as binary search trees.
. This is also known as the Hu-Tucker problem, after the authors of the paper presenting the first linearithmic solution to this optimal binary alphabetic problem, which has some similarities to Huffman algorithm, but is not a variation of this algorithm. These optimal alphabetic binary trees are often used as binary search trees.
The canonical Huffman code
If weights corresponding to the alphabetically ordered inputs are in numerical order, the Huffman code has the same lengths as the optimal alphabetic code, which can be found from calculating these lengths, rendering Hu-Tucker coding unnecessary. The code resulting from numerically (re-)ordered input is sometimes called the canonical Huffman code and is often the code used in practice, due to ease of encoding/decoding. The technique for finding this code is sometimes called Huffman-Shannon-Fano coding, since it is optimal like Huffman coding, but alphabetic in weight probability, like Shannon-Fano coding. The Huffman-Shannon-Fano code corresponding to the example is 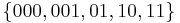 , which, having the same codeword lengths as the original solution, is also optimal.
, which, having the same codeword lengths as the original solution, is also optimal.
Model reconstruction
Decompression generally requires transmission of information in order to reconstruct the compression model (methods such as adaptive Huffman do not, although they typically produce less than optimal code lengths). Originally, symbol frequencies were passed along to the decompressor, but this method is very inefficient, as it can produce an unacceptable level of overhead. The most common technique utilizes canonical Huffman encoding, which only requires 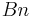 bits of information (where
bits of information (where  is the number of bits per symbol and
is the number of bits per symbol and 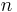 is the size of the symbol's alphabet). Other methods, such as the "direct transmission" of the Huffman tree, produce variable-length encoding of the model which can reduce the overhead to just a few bytes, in some cases.
is the size of the symbol's alphabet). Other methods, such as the "direct transmission" of the Huffman tree, produce variable-length encoding of the model which can reduce the overhead to just a few bytes, in some cases.
Because the compressed data can include unused "trailing bits", the decompressor must be able to determine when to stop producing output. This can be accomplished by either transmitting the length of the decompressed data along with the compression model or by defining a special code symbol to signify the end of input (the latter method can adversely affect code length optimality, however).
Applications
Arithmetic coding can be viewed as a generalization of Huffman coding; indeed, in practice arithmetic coding is often preceded by Huffman coding, as it is easier to find an arithmetic code for a binary input than for a nonbinary input. Also, although arithmetic coding offers better compression performance than Huffman coding, Huffman coding is still in wide use because of its simplicity and high speed.
Huffman coding today is often used as a "back-end" to some other compression method. DEFLATE (PKZIP's algorithm) and multimedia codecs such as JPEG and MP3 have a front-end model and quantization followed by Huffman coding (or variable-length prefix-free codes with a similar structure, although perhaps not necessarily designed by using Huffman's algorithm).
See also
- Adaptive Huffman coding
- Canonical Huffman code
- Huffyuv
- Modified Huffman coding - used in fax machines
- Shannon-Fano coding
- Polar tree
- Data compression
- Lempel–Ziv–Welch
- Varicode
References
- Huffman's original article: D.A. Huffman, "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes", Proceedings of the I.R.E., September 1952, pp 1098–1102
- Background story: Profile: David A. Huffman, Scientific American, September 1991, pp. 54–58
- Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN 0-262-03293-7. Section 16.3, pp. 385–392.
External links
- Program for explaining the Huffman Coding procedure.
- n-ary Huffman Template Algorithm
- Sloane A098950 Minimizing k-ordered sequences of maximum height Huffman tree
- Mordecai J. Golin, Claire Kenyon, Neal E. Young "Huffman coding with unequal letter costs" (PDF), STOC 2002: 785-791
- Huffman Coding: A CS2 Assignment a good introduction to Huffman coding
- A quick tutorial on generating a Huffman tree
- Pointers to Huffman coding visualizations
- Huffman in C
- Description of an implementation in Python
- Explanation of Huffman coding with examples in several languages
- Interactive Huffman Tree Construction
- A C program doing basic huffman coding on binary and text files
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||